Paul Kim
Types of nerves and ganglia (Latin)
Types of nerves and ganglia (Latin)
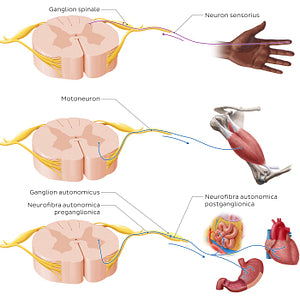
Nervi spinalis contain sensory and motor neurons. Sensory (or afferent) neurons carry information from the periphery to the systema nervosum centrale. The sensory axons enter the medulla spinalis as the radix posterior nervi spinalis. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the ganglion spinale, which is an enlargement of the nervus spinalis and is classified as a ganglion sensorium. The motor (or efferent) neurons carry information from the systema nervosum centrale to the periphery. The motor fibers, somatic and autonomic, emerge from the medulla spinalis as the radix anterior nervi spinalis. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the substantia grisea medullae spinalis. These impulses are conveyed through pre- and postganglionic autonomic (or visceral), efferent (or motor) nerve fibers. The synapse between these two types of neurons occurs in the ganglia autonomica, where the cell bodies of the postganglionic neurons are located.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability

#F4C737
#9E6A5E
#541F18
#54302A
#FBE36F
#D3ABCC

