Samantha Zimmerman
Sphenoid bone (posterior view) (Latin)
Sphenoid bone (posterior view) (Latin)
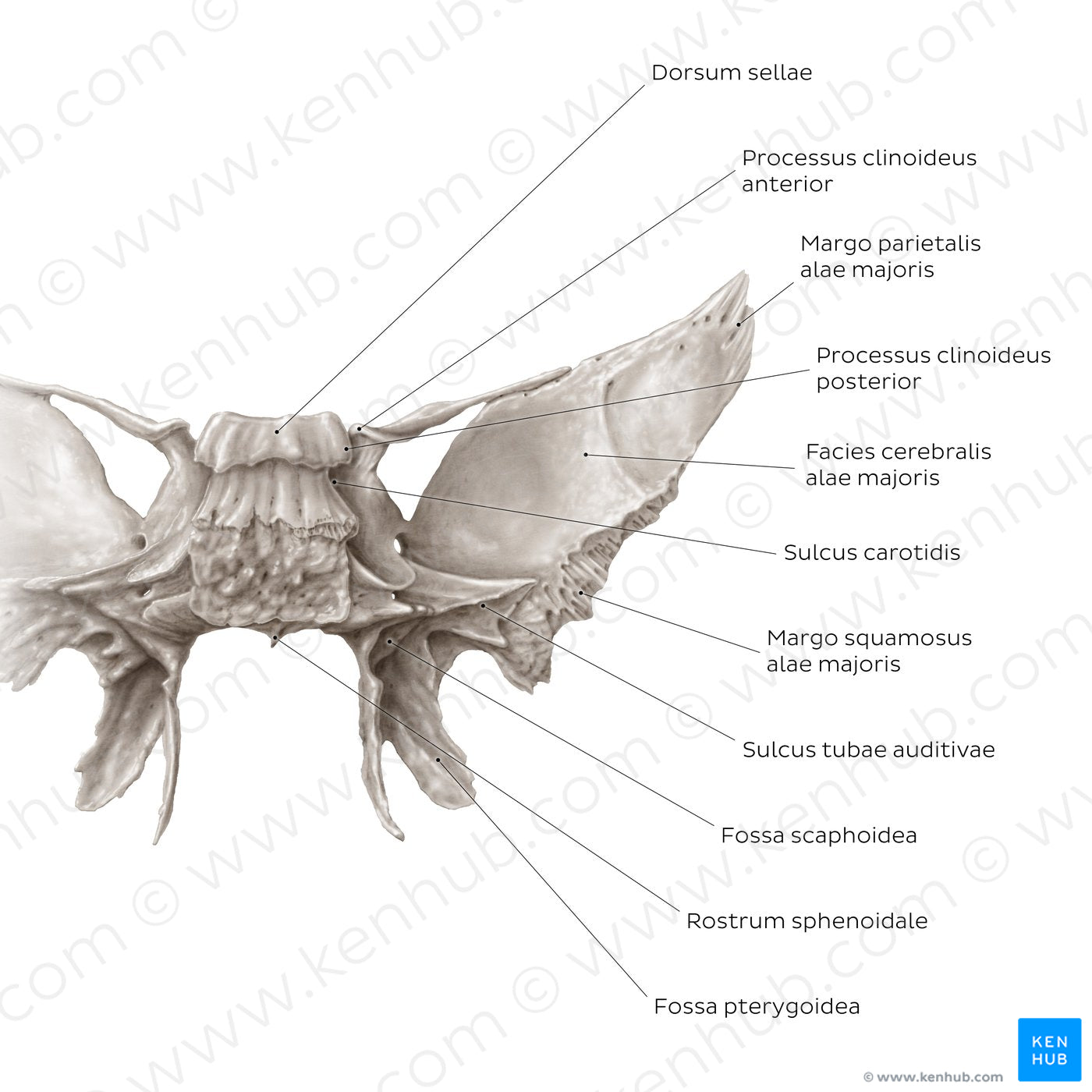
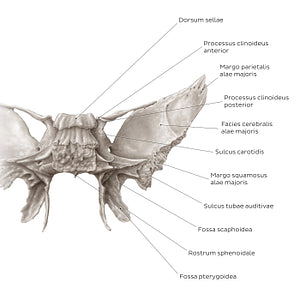
The posterior surface of the corpus is rough, featuring a prominent landmark: the dorsum sellae. The dorsum sellae articulates with the os occipitale and forms the clivus. The inferolateral angles of the dorsum present small processus clinoideus posterior, which forms one of the attachment points for the tentorium cerebelli. In the midline, the corpus presents a triangular process called the rostrum sphenoidale which points towards the ala vomeris. The posterior view allows a better appreciation of the root of the ala minor. This bony process spirals from the corpus, forming the processus clinoideus anterior, after which it continues laterally and fuses with the ala major. The irregular appearance of the root of the ala major is also noticeable from this perspective. This area features the sulcus tubae auditivae which houses the cartilaginous tuba auditiva. The facies cerebralis alae majoris contributes to the fossa cranii media, lodging a part of the lobus temporalis cerebri. The ridged margo parietalis and margo squamosus alae majoris are visible, which serve for the articulations with the os parietale and os temporale respectively.From this aspect, the laminae processus pterygoidei present as concave. At their origin there is a shallow fossa scaphoidea which serves as the attachment site for the m. tensor veli palatini. The very concavity of the lamina lateralis comprises an obtuse-angled fossa pterygoidea which provides the attachment site for the m. pterygoideus medialis.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability
#897C73
#4D4137
#C5BCB4

