Paul Kim
Muscles of thoracic wall (Posterior view) (English)
Muscles of thoracic wall (Posterior view) (English)
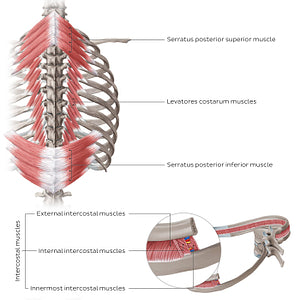
The intrinsic muscles of the posterior thoracic wall can be better appreciated from this view. The serratus posterior superior and inferior muscles (right) are two paired muscles located in the upper and lower back. Their main function is to facilitate the act of respiration; the serratus posterior superior muscle elevates the ribs, while the serratus posterior inferior muscle depresses the ribs. The levatores costarum consists of 12 small triangular bilateral muscles that connect the thoracic vertebrae with the adjacent ribs. This group of muscles function in elevating the ribs to facilitate forced inspiration and produce rotation and lateral flexion of the thoracic vertebrae. The external, internal and innermost intercostal muscles can also be appreciated from a posterolateral view of the thoracic cage (left). The external intercostal muscles are the most superficial intercostal muscles; their fibers are oriented in an inferomedial direction. The internal intercostal muscles form the middle layer of the intercostal musculature; their fibers course inferolaterally. The innermost intercostals are the deepest intercostal muscles and course in the same manner as the internal intercostal muscles. All three intercostal muscles are accessory respiratory muscles that participate in the process of forced breathing.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability

#C79437
#AA615F
#9D3736
#523832
#E4928F
#CFAFAD

