Yousun Koh
Muscles of the hand: Groups (English)
Muscles of the hand: Groups (English)
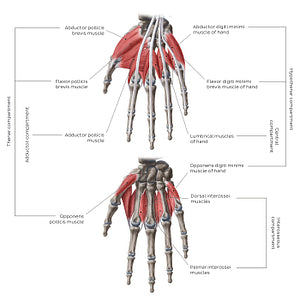
The muscles of the thenar compartment form the thenar eminence on the lateral aspect of the palm of the hand. The opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis muscles extend from the flexor retinaculum and tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium carpal bones, to attach to the 1st metacarpal or phalanx of the thumb. This group of muscles is largely responsible for creating opposition of the thumb.The adductor pollicis muscle of the adductor compartment is composed of two heads: an oblique and a transverse head. The oblique head arises from the base of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bones, while the transverse head originates from the anterior surface of the shaft of the 3rd metacarpal. Both heads extend to insert onto the base of the 1st proximal phalanx. This muscle group is responsible for adduction of the thumb. The muscles of the hypothenar compartment form the hypothenar eminence on the medial aspect of the palm of the hand. The abductor digiti minimi muscle arises from the pisiform bone, while the flexor digiti minimi brevis and opponens digiti minimi muscles both arise from the hook of the hamate and the flexor retinaculum on the lateral aspect of the hand. The hypothenar muscles extend to insert onto either the 5th metacarpal or proximal phalanx and function to facilitate opposition of the little finger. The central compartment is made up of the lumbrical muscles. The lumbricals (4) are found between the metacarpals, but unlike dorsal and palmar interossei, they do not attach to the metacarpal bones, and instead attach proximally to the tendons of flexor digitorum profundus muscle.The interosseous compartment is composed of the palmar and dorsal interossei muscles. The interossei muscles attach to the metacarpals and extend to insert onto the proximal phalanges of associated fingers. The palmar interossei muscles function to adduct the 2nd, 4th and 5th digits towards the axial line, while the dorsal interossei muscles function to abduct the 2-4th digits away from the axial line.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability

#B14F4E
#A8615D
#6B1818
#473931
#E79997
#CDB2AE

