Paul Kim
Cranial nerve nuclei - posterior view (efferent) (English)
Cranial nerve nuclei - posterior view (efferent) (English)
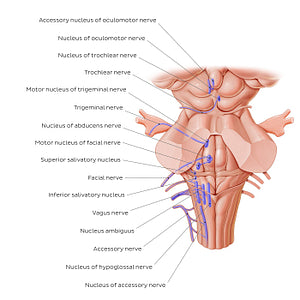
The nuclei of origin of efferent (motor) fibers are organized into discontinuous longitudinal columns within the brainstem. The general somatic efferent nuclei lie closest to the midline and are made up of the oculomotor, trochlear, abducens and hypoglossal cranial nerve nuclei. These nuclei can also be identified from a sagittal view (see next image). The oculomotor and trochlear nuclei are located in the midbrain at the level of the superior and inferior colliculi. The abducens nucleus lies in the lower part of the pons, while the hypoglossal nucleus is situated within the lower medulla oblongata. These nuclei are composed of lower motor neurons and are responsible for innervating striated (skeletal) muscles of somatic origin, specifically the voluntary muscles of the eye and tongue. Special visceral efferent nuclei, also known as the branchial efferent or branchiomotor nuclei, are made up of the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve, the nucleus of the facial nerve and the nucleus ambiguus (See next image to identify these nuclei from a sagittal perspective). The motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve and the nucleus of the facial nerve are located in the pons, while the nucleus ambiguus is situated in the medulla oblongata. The nucleus ambiguus communicates with the glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves. The special visceral efferent nuclei function to supply striated (skeletal) muscles derived from the branchial arches such as the stylopharyngeus muscle or some of the muscles of facial expression.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability

#CE5836
#6350AB
#9E311F
#492343
#E99D8D
#D2B0AC

