Paul Kim
Corticospinal tract (Latin)
Corticospinal tract (Latin)
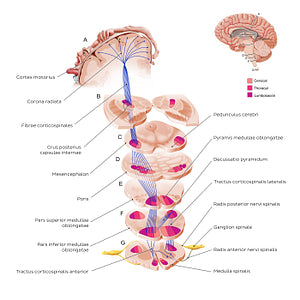
The corticospinal tract originates from upper motor neurons (UMN) located in the primary motor cortex. The arising fibers form the corona radiata and converge to pass through the crus posterior capsulae internae into the truncus encephali (brainstem). The fibers here pass through the pedunculus cerebri, the pons, and the pyramis medullae oblongatae, from which the pyramidal tracts got their name. At the level of the pars inferior medullae oblongatae, the majority (90%) of the fibrae corticospinales cross over to the opposite side, an action deemed as the decussatio pyramidum. The fibers that cross over continue as the tractus corticospinalis lateralis. About 10% of the fibers that remained on the same side continue as the tractus corticospinalis anterior. However, these fibers ultimately do decussate at the lower levels of medulla spinalis, close to their destination. At this point, the upper motor neurons (UMN) of both the tractus corticospinalis lateralis and anterior synapse with the lower motor neurons (LMN) in the anterior gray horn of each level of the medulla spinalis. The lower motor neurons then leave the medulla spinalis through the radix anterior nervi spinalis to form peripheral nerves, which innervate the muscles of the trunk and limbs.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability

#ED2F76
#A9685C
#B30E76
#746D6D
#F6D35A
#D3B3AD

