Paul Kim
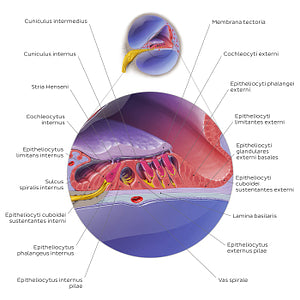
Cochlear duct/spiral organ: cross section (Latin)
Cochlear duct/spiral organ: cross section (Latin)
The organum spirale (of Corti) is the receptor organ for hearing that produces electrical impulses in response to auditory stimuli. It is located in the scala media of the canalis cochlearis sitting on top of the lamina basilaris. The organum spirale (of Corti) is composed of receptor cells known as the cochleocyti (hair cells). It contains three rows of cochleocyti externi and one row of cochleocytus internus. The hair cells are so named because they contain hair-like projections on the apical part of their cell membrane, known as stereocilia. The stereocilia are embedded in a gel-like structure called the membrana tectoria. The lower surface of the membrana tectoria harbours a longitudinal ridge called the stria Henseni that anchors the membrana tectoria to the epitheliocytus limitans internus and externus (inner and outer border cells). As the perilymph moves in response to sound waves, it shifts the lamina basilaris respectively to the membrana tectoria. These shifts between the membrana tectoria and lamina basilaris bend the stereocilia, causing the cochleocyti (hair cells) to depolarize and release the neurotransmitters (glutamate) that transmits the sound information to the n. cochlearis. Aside from the hair cells, the spiral organ (of Corti) contains a number of epitheliocyti sustenans (supporting cells). From the outer edge to the inner edge of the organ, these are: epitheliocyti cuboidei sustentantes externi (Claudius cells), epitheliocyti limitantes externi (Hensen’s cells), epitheliocyti phalangei externi (Deiters’ cells), epitheliocytus internus and externus pilae, epitheliocytus phalanges internus and epitheliocyti limitantes. These supporting cells have distinct morphologies in relation to their functions. The epitheliocyti phalangei internus and externus surround and support the basolateral parts of both cochleocyti externi and interni. Between the outer and inner complexes of cochleocyti and epitheliocyti phalangei, there is a cavity known as the cuniculus internus (inner tunnel of Corti). This tunnel is formed by the arching epitheliocytus internus and externuspilae.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability

#D5A920
#715AA5
#581946
#4D2E53
#D78A8D
#B2ADCE

