Paul Kim
Cochlea: cross section (Latin)
Cochlea: cross section (Latin)
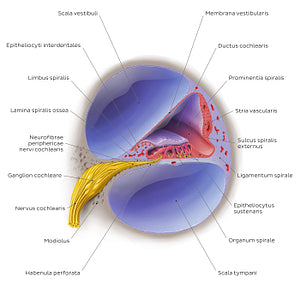
The cochlea is the structure of the auris interna responsible for hearing. Its structure resembles a snail shell situated in the labyrinthus osseus of the os temporale. The 'shell' of the cochlea is wrapped 2.75 times around its axis called the modiolus. The cross section of the cochlea reveals its internal structure which is characterized by the bony cavity of the cochlea (canalis spiralis cochleae) and a triangular membranous duct, called the ductus cochlearis (also known as the scala media). The scala media is filled with endolympha. In addition to the scala media, there are two more canals that run parallel to one another including the scala vestibuli and scala tympani. In contrast to the scala media, the scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with perilympha. Sound vibrations transmitted from the auris media through the fenestra vestibularis result in mechanical movements of the fluids inside the cochlea which moves the lamina basilaris. Movements of the lamina basilaris in turn cause movements of the structures within the cochlear duct. These movements are converted to electrical impulses in the receptor part of the cochlea known as the organum spirale (organum Cortii)
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability

#F0C92D
#A75C66
#A6720C
#392B54
#F4E396
#ACADD3

