Rebecca Betts
Arteries of the spinal cord (Latin)
Arteries of the spinal cord (Latin)
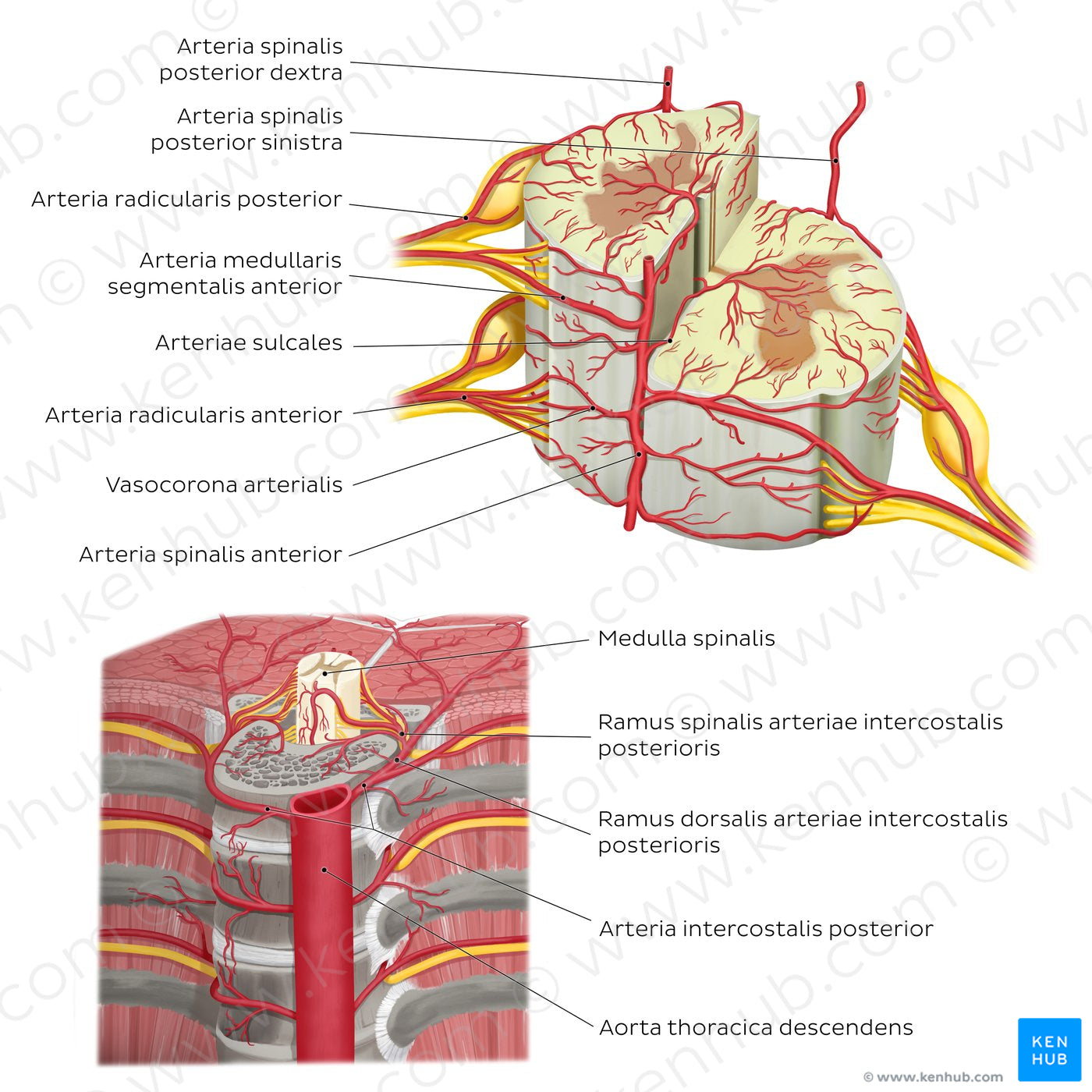
The medulla spinalis and its roots and nerves are supplied with arterial blood by longitudinal and segmental vessels. The longitudinal vessels are the single a. spinalis anterior and paired a. spinalis posterior, that arise from the a. vertebralis and terminate near the conus medullaris. The a. spinalis anterior descends in the fissura mediana anterior and gives off the aa. sulcales, which enter the substance of the medulla spinalis. The a. spinalis anterior provides blood to the anterior two-thirds of the medulla spinalis, supplying the cornu anterior, cornu lateralis, substantia grisea centralis, funiculus anterior and funiculus lateralis medullae spinalis. The two aa. spinales posteriores arise mainly from the a. vertebralis, but they can also arise from the a. inferior cerebelli. The aa. spinales posteriores descend in the two sulci posterolaterales. It provides blood to the posterior third of the medulla spinalis, supplying the cornu posterior and funiculus posterior medullae spinalis. The a. spinalis anterior and aa. spinales posteriores form pial anastomoses called the vasocorona arterialis, which encircles the medulla spinalis and supplies its lateral surface and the spinal meninges. Each segment of the medulla spinalis receives additional supply from the segmental vessels that arise from different sources depending on the region. These arteries pass through the foramina intervertebralia into the columna vertebralis, where they split into the a. radicularis anterioris and posterioris and pass along the radix anterior and radix posterior nervi spinalis (roots of spinal nerves). Most of the aa. radiculares are small and end their course in the nerve roots. However, some larger radicular branches give off the aa. medullares (segmental medullary arteries) that feed into the a. spinalis anterior and posterior.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability
#F5D123
#AD635B
#B31828
#62372F
#F4DC5E
#CDB1AC

