Yousun Koh
Arteries of the arm and the shoulder - Posterior view (Latin)
Arteries of the arm and the shoulder - Posterior view (Latin)
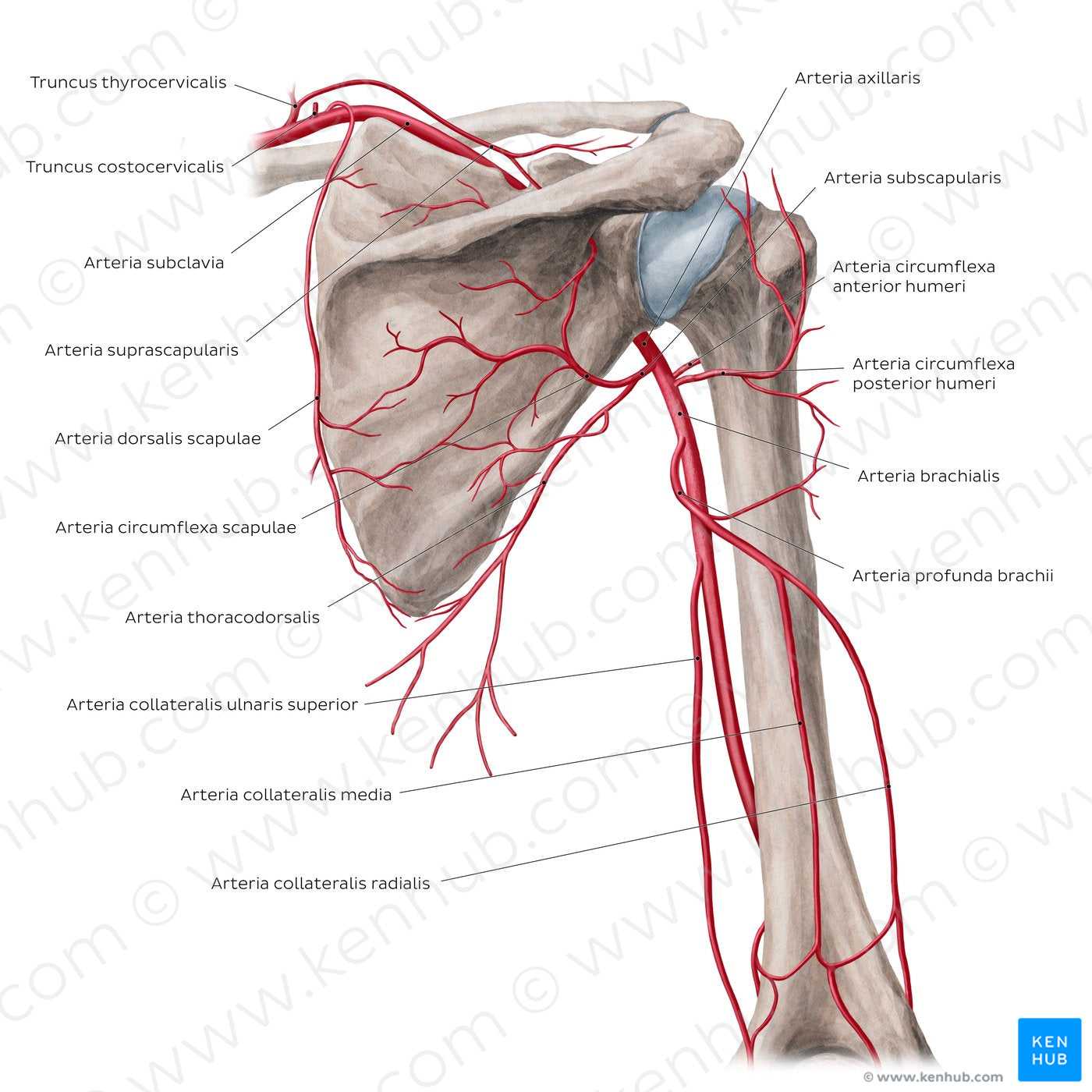
Oxygenated blood is supplied to the proximal upper limb by arterial branches originating from the a. subclavia. The truncus thyrocervicalis, a short and wide vessel arising from the first segment of the a. subclavia, vascularizes the deep cervical and shoulder muscles as well as the skin of the neck (collum) and shoulders (omos). A branch of the truncus thyrocervicalis, the a. suprascapularis, courses inferolaterally towards the margo superior of the scapula to supply muscles in the shoulder and scapular region, including skin of the upper thoracic cage and shoulder. The a. dorsalis scapulae, an independent branch of the a. subclavia, supplies two superficial muscles of the back, the levator scapulae and m. rhomboideus major/minor. It anastomoses with the a. suprascapularis in the posterior scapular region. Together with the a. subscapularis and its branch, the a. circumflexa scapulae, they form the rete scapulae. The a. thoracodorsalis, a branch of the a. subscapularis, descends with the n. thoracodorsalis to supply muscles of the back and skin in the axillary region. The largest branch of the a. brachialis is the a. brachialis profunda which supplies the posterior arm muscles. It divides into two branches, the a. collateralis media and a. collateralis radialis which contribute to the rete articulare cubiti. Specifically, the a. collateralis radialis supplies the n. radialis, the m. brachioradialis and m. brachialis.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability
#A80415
#9F565A
#95030B
#5A292B
#E65C72
#CDB3AC

