Paul Kim
12 cranial nerves (English)
12 cranial nerves (English)
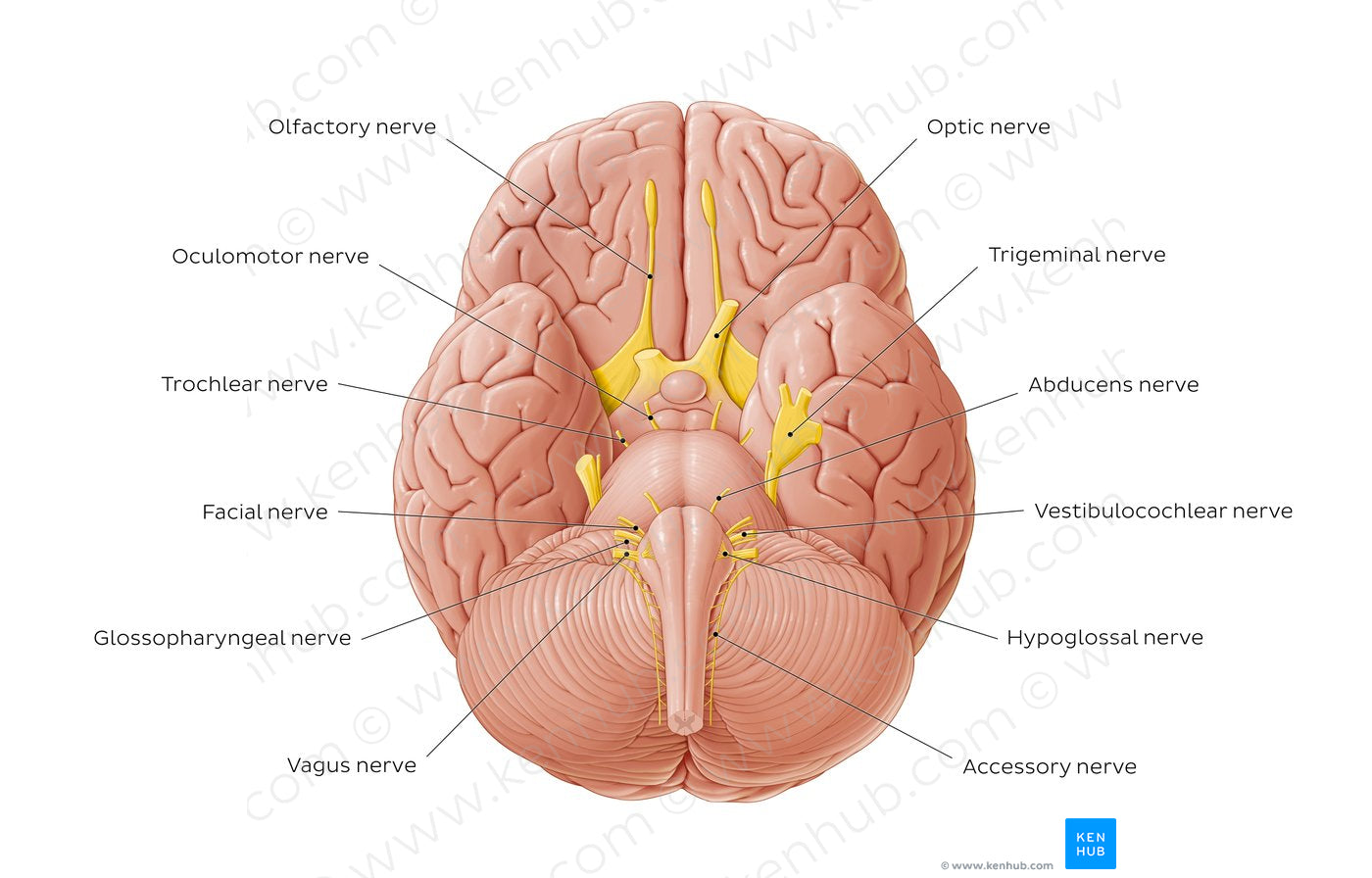
This illustration summarizes the anatomy of each cranial nerve. The first two cranial nerves, the olfactory nerve (CN I) and optic nerve (CN II) are the only two cranial nerves that originate from the cerebrum. More specifically, the olfactory nerve (CN I) can be generally used as an umbrella term to describe components extending from the olfactory part of the nasal mucosa to the olfactory cortex (via the cribriform plate of ethmoid bone). The optic nerve (CN II) extends from the retina of the eye to the primary visual cortex (striate area) via the optic canal. All other cranial nerves originate from the brainstem. The oculomotor (CN III) and trochlear (CN IV) nerves originate from the midbrain. The abducens nerve (CN VI) originates from the pontomedullary region. Since these three nerves act on eye muscles, they extend from the brainstem and exit via the superior orbital fissure. The trigeminal nerve (CN V) originates from the pons and gives rise to three nerve divisions: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) which exit the cranium via the superior orbital fissure, foramen rotundum and foramen ovale, respectively. The facial nerve (CN VII) originates from the pontomedullary junction by two roots: motor and sensory. The vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) also originates from the pontomedullary junction and consists of the vestibular and cochlear components. Both CN VII and VIII exit via the internal acoustic meatus. The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) originates from the superior/rostral portion of the medulla oblongata while the vagus nerve (CN X) also originates from the medulla oblongata, just caudal to CN IX. The accessory nerve (CN XI) has traditionally been described as having both spinal and cranial roots. As seen in the illustration, its cranial root emerges from the medulla oblongata, while the spinal root arises from the upper five or six cervical segments of the spinal cord. CN IX-XI all exit the skull via the jugular foramen. Finally, the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) also originates from the medulla oblongata. Its dozen roots pass laterally across the posterior cranial fossa before merging into a single trunk which exits via the hypoglossal canal.
Regular price
$7.56 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$7.56 USD
Unit price
per
Couldn't load pickup availability
#F1CA2E
#B09656
#B48A19
#96624E
#F4D56C
#D8B0A6

