Paul Kim
Vestibulocochlear nerve (English)
Vestibulocochlear nerve (English)
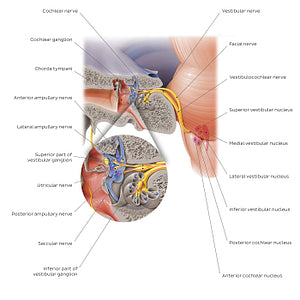
The vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) arises from the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction/cerebellopontine angle. It exits the cranium via the internal acoustic meatus of the temporal bone, where it divides into the vestibular and cochlear nerves. The vestibular nerve contains the axons of neurons whose cell bodies are found in the vestibular ganglion, found at the lateral end/fundus of the internal acoustic meatus. The vestibular ganglion consists of superior and inferior parts, from which the superior and inferior branches of vestibular nerve arise and proceed to innervate the vestibular apparatus (utricle, saccule and semicircular ducts). The anterior ampullary, lateral ampullary and utricular nerves arise from the superior branch, while the posterior ampullary and saccular nerves are given off from the inferior component. These nerves collect the information related to motion and position of the head and transmit it to the vestibular nuclei (the superior, inferior, medial and lateral vestibular nuclei) in the lower pons/upper medulla oblongata in order to maintain balance and equilibrium. The cochlear nerve contains the axons of neurons whose cell bodies are located in the cochlear/spiral ganglion that lies in the spiral canal of the modiolus of the cochlea. Peripheral processes of these neurons send terminal endings to receptors in the spiral organ (of Corti), that collect auditory information and transmit it via the cochlear nerve to the cochlear nuclei (anterior and posterior cochlear nuclei) in the brainstem, and ultimately to the primary auditory cortex of the temporal lobe.
Precio habitual
$7.56 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$7.56 USD
Precio unitario
por
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro

#D6A527
#5E6CA4
#612E25
#624935
#F1DF90 y #C8B8AF

