Liene Znotina
Typical thoracic vertebra (Latin)
Typical thoracic vertebra (Latin)
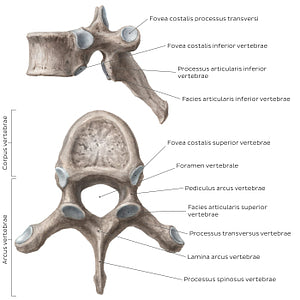
A typical vertebra thoracica consists of a corpus vertebrae, arcus vertebrae, processus spinosus, transversus as well as processus articulares superior et inferior vertebrae. The corpus vertebrae (typically heart-shaped) is larger than those seen in the columna vertebralis cervicalis, but smaller than those of the vertebrae lumbales. Specific features of vertebrae thoracicae are detailed below.Foveae costales: Vertebrae T2-T9 bear a fovea costalis superior et inferior which are located on the margo superior/inferior of the lateral sides of each corpus vertebrae (therefore, articulation with the caput costae is shared between adjacent vertebrae). Vertebra T1 features a fovea costalis inferior along its inferolateral margins, and a whole facet on its superolateral surfaces. Vertebrae T10-T12 features a single whole fovea costalis on each side of their corpus vertebrae.Arcus vertebrae: The arcus vertebrae in vertebrae thoracicae are more cylindrical and smaller than that in vertebrae cervicales. Processus spinosus: The processus spinosus of vertebrae thoracicae are elongated, with the angle between the processus spinosus and the corpus vertebrae becoming more acute in lower levels.Processus transversus: Each processus transversus features foveae costales for articulation with the tuberculum costae of the ipsilateral numerically equivalent costa (exception: vertebrae T11/T12).Processus articulares superior et inferior: Each processus articularis superior faces backward (and slightly lateral/upwards), while each processus articularis inferior is oriented forward (and slightly medial/downward).
Precio habitual
$7.56 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$7.56 USD
Precio unitario
por
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro

#91806E
#473D35
#E1D2BF y #CFC0AD

