Paul Kim
Spinal cord: Cross section (ascending and descending tracts) (Latin)
Spinal cord: Cross section (ascending and descending tracts) (Latin)
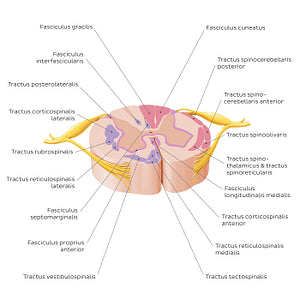
The substantia alba medullae spinalis is made of myelinated nerve fibers organized into ascending, descending and intersegmental tracts. Ascending tracts are formed of primary afferent fibers which enter through radix posterior nervi spinalis. They can be divided into three distinct pathways: the anterolateral system, the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway and the somatosensory pathways to the cerebellum. The anterolateral system includes the tractus spinothalamici, tractus spinoreticularis and tractus spinoolivaris which function to relay sensations of pain, temperature and non-discriminative touch. The posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway is formed by the fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus and relays discriminative touch, vibration, pressure and proprioception. Finally the somatosensory pathways to the cerebellum are composed of the tractus spinocerebellaris anterior, posterior and rostralis, which function to relay proprioception as well as sensations of pain and pressure. Descending tracts are formed of efferent fibers that carry motor information from the brain (encephalon) or brainstem (truncus encephali) to effector’s muscles. They can be functionally divided into two groups: tractus pyramidalis (voluntary) and tractus extrapyramidalis (involuntary). The tractus pyramidalis originates in the cortex cerebri and carries motor fibers to the brainstem (truncus encephali) and medulla spinalis. They include the tractus corticospinalis anterior and lateralis. The tractus extrapyramidalis begins within the brainstem (truncus encephali) and carries motor fibers to the medulla spinalis. They include the tractus tectospinalis, tractus reticulospinalis medialis, tractus vestibulospinalis, tractus reticulospinalis lateralis and the tractus rubrospinalis. The tractus pyramidalis is responsible for voluntary control of the muscles of the body, while tractus extrapyramidalis is responsible for the involuntary and automatic control.Intersegmental tracts are short ascending and descending tracts which begin and end within the medulla spinalis. They function to interconnect neurons at different spinal segments and are important in intersegmental spinal reflexes. Intersegmental tracts are composed of the fasciculus posterolateralis, the fasciculus longitudinalis medialis, the fasciculus septomarginalis and the fasciculus interfascicularis.
Precio habitual
$7.56 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$7.56 USD
Precio unitario
por
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro

#DC9E23
#A07792
#DC9E23
#60535B
#FCE372 y #CFB3AB

