Yousun Koh
Radius and ulna: Anterior view (Latin)
Radius and ulna: Anterior view (Latin)
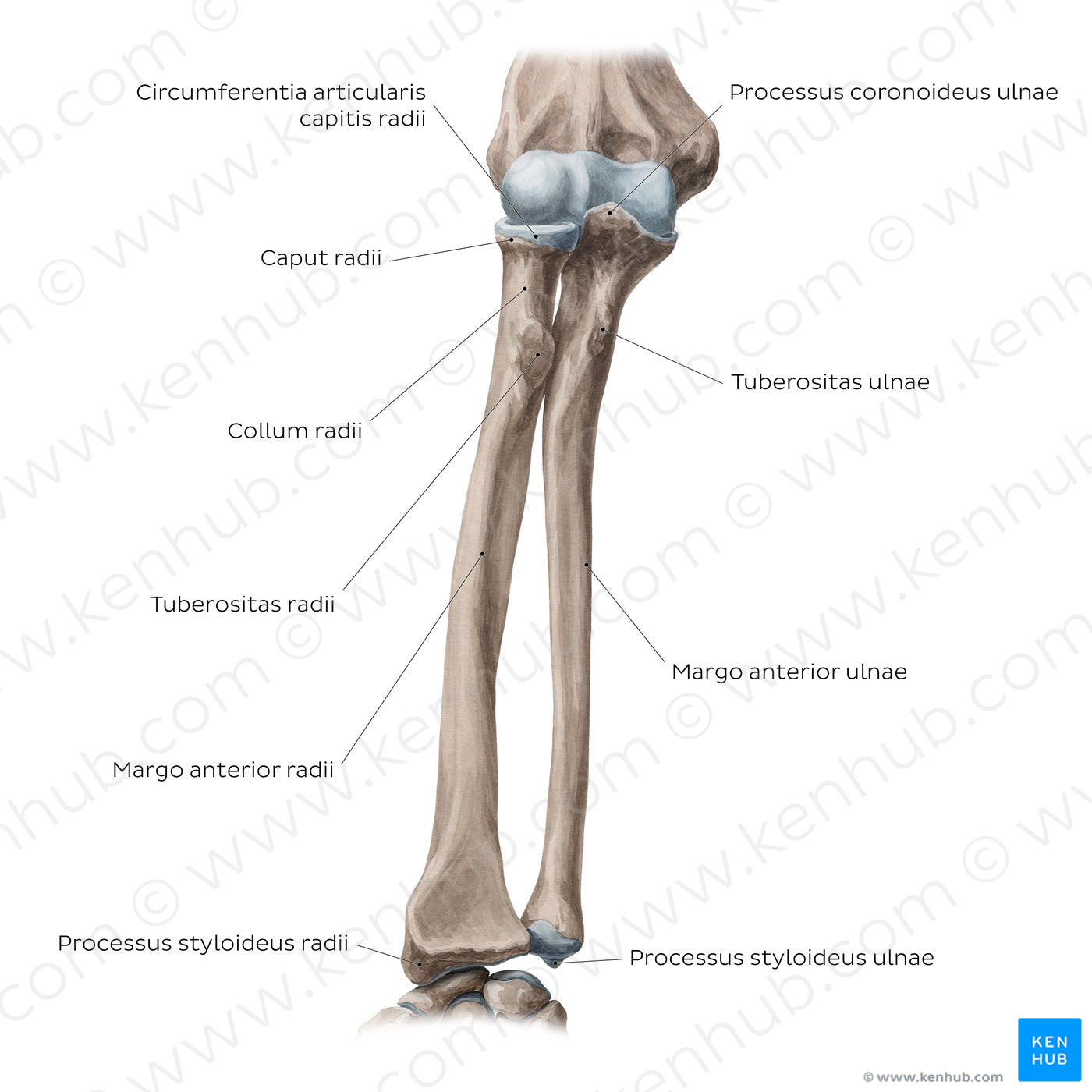
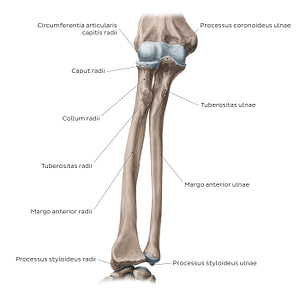
The radius is the shorter of the two bones of the forearm (antebrachium) and consists of a proximal extremity, shaft and a distal extremity. The proximal end of radius consists of a head and neck. The discoid caput radii articulates superiorly with the capitulum of the humerus, contributing to the formation of the elbow joint (art. cubiti). At the same time, the caput radii also articulates with the ulna forming the proximal radioulnar joint (art. radioulnaris proximalis). In this joint, the circumference of the caput radii is situated on the incisura radialis. The collum radii is a narrowing of the radius that lies just distal to the caput radii. Distal to the medial aspect of the collum radii is an oval bony protrusion known as the tuberositas radii, onto which the mm. biceps brachii inserts. The corpus radii acts as an important attachment point for muscles of the forearm, some of which include the mm. supinator and pronator teres. From this anterior view, the margo anterior radii of the corpus radii can be appreciated. The distal extremity of the radius widens to form three smooth, concave surfaces. The medial aspect of the distal radius forms a concavity known as the incisura ulnaris, which articulates with the distal ulna. The lateral aspect of the distal radius forms a ridge and terminates distally as the processus styloideus radii. The ulna is similarly composed of a proximal end, shaft and distal end. The proximal end of the ulna is particularly wide to accommodate the trochlea humeri. Projecting anteriorly from the proximal portion of the ulna is the processus coronoideus. The processus coronoideus aids in stabilizing the elbow joint and preventing hyperflexion of the forearm. Inferior to the processus coronoideus is the tuberositas ulnae, which functions as an attachment point for the m. brachialis. The distal end of the ulna tapers to form the disc-like caput ulnae. The caput ulnae does not articulate with the ossa carpi and is therefore not a component of the wrist joint (carpus). Projecting from the caput ulnae is a small bony protrusion known as the processus styloideus ulnae.
Precio habitual
$7.56 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$7.56 USD
Precio unitario
por
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro
#8C796D
#4A3A31 y #D1BEB0

