Yousun Koh
Nerves of the pharynx (Latin)
Nerves of the pharynx (Latin)
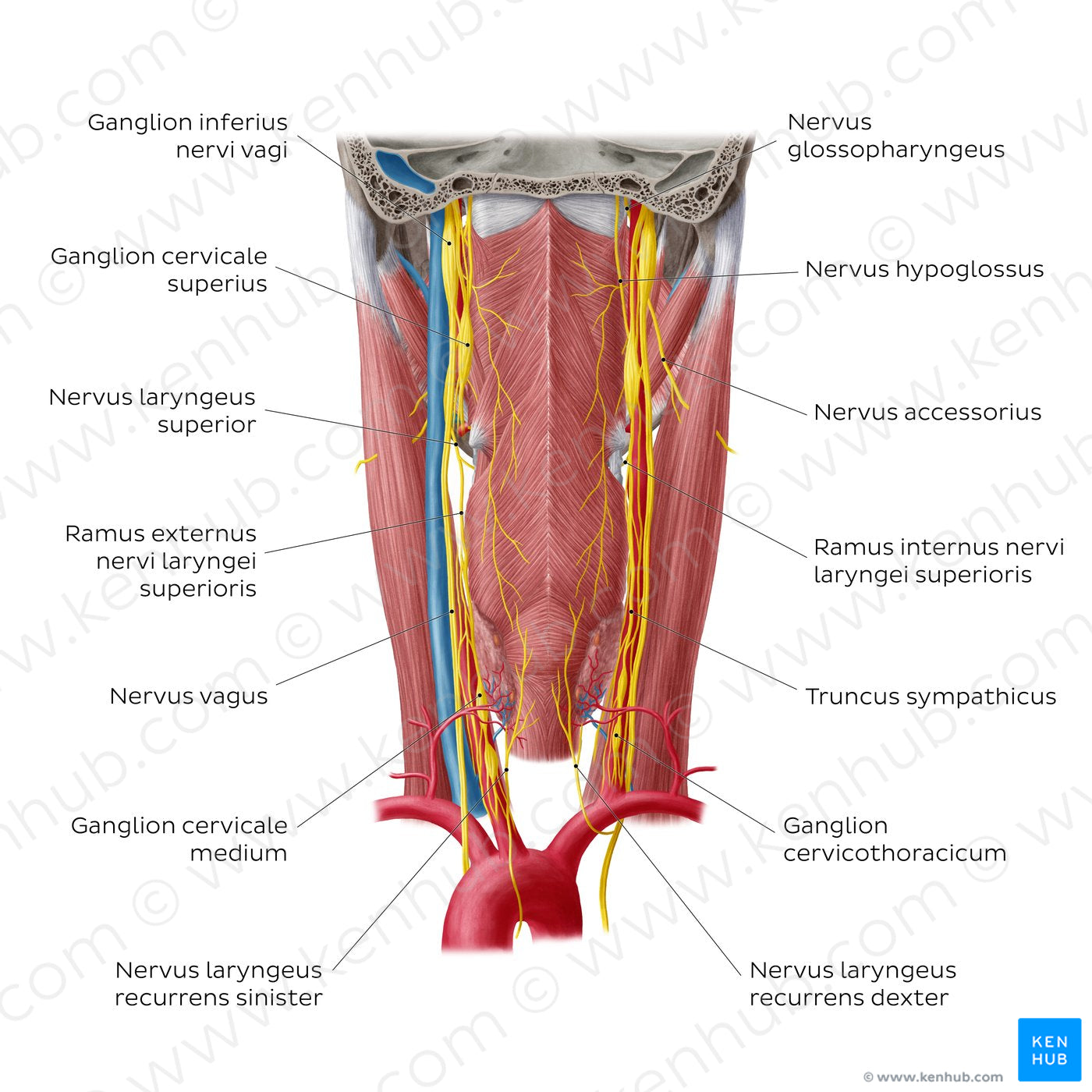
In this posterior view we can see the nerves that supply the pharynx and other important nervous structures of the spatium parapharyngeum. The plexus pharyngeus is mainly composed of pharyngeal branches of the n. glossopharyngeus and n. vagus. This plexus lies on the external surface of the pharynx. On the right side of the image, superiorly, we have a glimpse of the n. glossopharyngeus (CN IX) after leaving the skull through the foramen jugulare. The n. vagus (CN X) also leaves the skull through this foramen and has two sensory ganglia in this location - in this image we can see the ganglion inferius. The n. laryngeus superior arises from the ganglion inferius of the n. vagus and descends against the lateral wall of the pharynx. It divides into the ramus externus and ramus internus. The n. laryngeus recurrens is also a branch of the n. vagus that supplies the larynx. The right and left nerves are not symmetrical, with the left nerve looping under the arcus aortae, and the right nerve looping under the a. subclavia dextra then traveling upwards. The n. accessorius (CN XI) also passes through the foramen jugulare and courses through the neck; it pierces the m. sternocleidomastoideus which it innervates. The n. hypoglossus (CN XII) leaves the skull, travels down the neck and ends at the base and underside of the tongue, being responsible for its nerve supply. The cervical truncus sympathicus lies behind the vagina carotidis (a condensation of deep fascia of the neck in which is embedded the a. carotis communis and interna, v. jugularis interna, and the n. vagus). This trunk contains three interconnected ganglia: the superius, medium and inferius (stellate or cervicothoracicum).
Precio habitual
$7.56 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$7.56 USD
Precio unitario
por
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro
#ECD124
#AB5655
#950610
#5F2F2B
#F0E05A y #CFB2AE

