Paul Kim
Eye in situ: sagittal section (Latin)
Eye in situ: sagittal section (Latin)
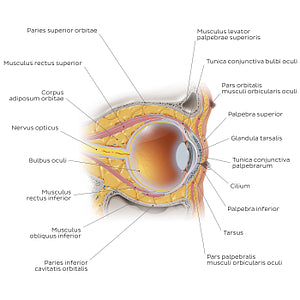
This image allows an appreciation of a number of accessory visual structures which support and protect the eyeball (bulbus oculi). The eyeball is suspended within the anterior portion of the orbita by six mm. externi bulbi oculi and by a vagina bulbi. There are seven mm. externi bulbi oculi altogether which can be divided into four mm. recti, two mm. obliqui and one mm. levator palpebrae superioris. The mm. levator palpebrae superioris attaches to the palpebra superior and functions to raise and maintain it in an open position. The other six mm. externi bulbi oculi extend to insert onto the sclera of the eyeball and are responsible for controlling movement. Lying against the anterior aspect of the eyeball are the tunica conjunctiva palpebrae and eyelids (palpebrae), as well as their associated glands which protect the eyeball from the external environment. Surrounding the eyeball is a mass of adipose tissue known as corpus adiposum orbitae. It functions to cushion and support the eyeball within the orbit and prevent excessive posterior pull on the eyeball by the mm. recti. Extending from the posterior aspect of the bulbus oculi is the a./v. centralis retinae which pierces the n. opticus before it reaches the bulbus oculi. The n. opticus exits the orbita through the canalis opticus and transmits sensory information from the oculus to the brain.
Precio habitual
$7.56 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$7.56 USD
Precio unitario
por
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro

#C5370F
#A66957
#8A3C20
#4F3D36
#EACD8E y #CAB6B0

