Paul Kim
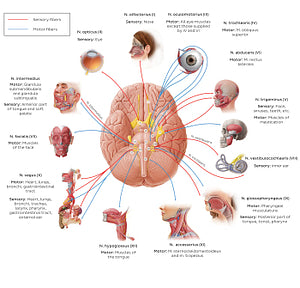
12 cranial nerves (diagram) (Latin)
12 cranial nerves (diagram) (Latin)
The n. olfactorius (CN I) is solely sensory and conveys impulses that provide the sense of smell (olfaction). The n. opticus (CN II) is also a sensory nerve, responsible for vision. The n. oculomotorius (CN III), n. trochlearis (CN IV) and n. abducens (CN VI) can be observed as a group due to their similar functions: all are motor nerves that innervate the eye muscles and thus play a key role in eye movement/accommodation. The n. trigeminus (CN V) is the first mixed nerve (i.e. has both sensory and motor fibers). This nerve provides the sensation for the face and controls the muscles of mastication. The n. facialis (CN VII) is also a mixed nerve. The function of the sensory portion of this nerve is to provide a taste for the anterior portion of the tongue, while its motor component plays part in the modulation of facial expressions, salivation, and lacrimation. The n. vestibulocochlearis (CN VIII) is a sensory nerve in charge of maintaining balance and hearing. The n. glossopharyngeus (CN IX) is a mixed nerve that provides sensation to the tongue and pharynx, as well as the control of muscles that facilitate the act of swallowing. The n. vagus (CN X) is the longest mixed cranial nerve. Its sensory role is to convey sensory information from the external ear, pharynx, larynx, thorax, and abdomen. In contrast, its motor component plays part in acts of swallowing, speech, coughing, and various parasympathetic functions. The n. accessorius (XI) is solely a motor nerve. It controls two muscles involved in head and shoulder movements (m. sternocleidomastoideus/ m. trapezius). The n. hypoglossal (CN XII) is also a motor nerve that controls muscles that facilitate the movements of the tongue.
Precio habitual
$7.56 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$7.56 USD
Precio unitario
por
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro

#DDAF2C
#965B54
#623121
#34201D
#EF928C y #D2B3AB

